Skin cancer is the most common form of cancer worldwide, affecting millions of people every year. Despite its prevalence, it is also one of the most preventable and treatable cancers when caught early. The key factor that makes a difference between life-saving treatment and advanced-stage challenges is early detection. Recognizing unusual changes in the skin, identifying high-risk individuals, and utilizing modern screening technologies are transforming the management of skin cancer. By focusing on early diagnosis, patients and healthcare systems can reduce mortality rates, improve quality of life, and lower the long-term costs associated with advanced treatment.
Understanding the Basics of Skin Cancer
Skin cancer begins when abnormal skin cells grow uncontrollably, often triggered by DNA damage from ultraviolet (UV) radiation. The two most common categories are non-melanoma skin cancers, such as basal cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma, and melanoma, which is less common but far more aggressive. While non-melanomas are often localized and treatable, melanoma has the potential to spread rapidly, making early detection crucial. Understanding the nature of these cancers helps individuals recognize why even a small mole or unusual skin spot should never be ignored.
The Importance of Early Diagnosis
Catching skin cancer at an early stage dramatically increases survival rates. For example, when melanoma is identified before it spreads beyond the skin, the five-year survival rate is above 90%. However, once it metastasizes to other organs, the prognosis declines significantly. Early diagnosis also enables less invasive treatments, a faster recovery, and lower healthcare costs. Patients diagnosed late often require more aggressive therapies such as chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or extensive surgery. This is why healthcare professionals emphasize awareness, regular screening, and timely medical intervention as the pillars of successful skin cancer management.
Recognizing Warning Signs and Symptoms
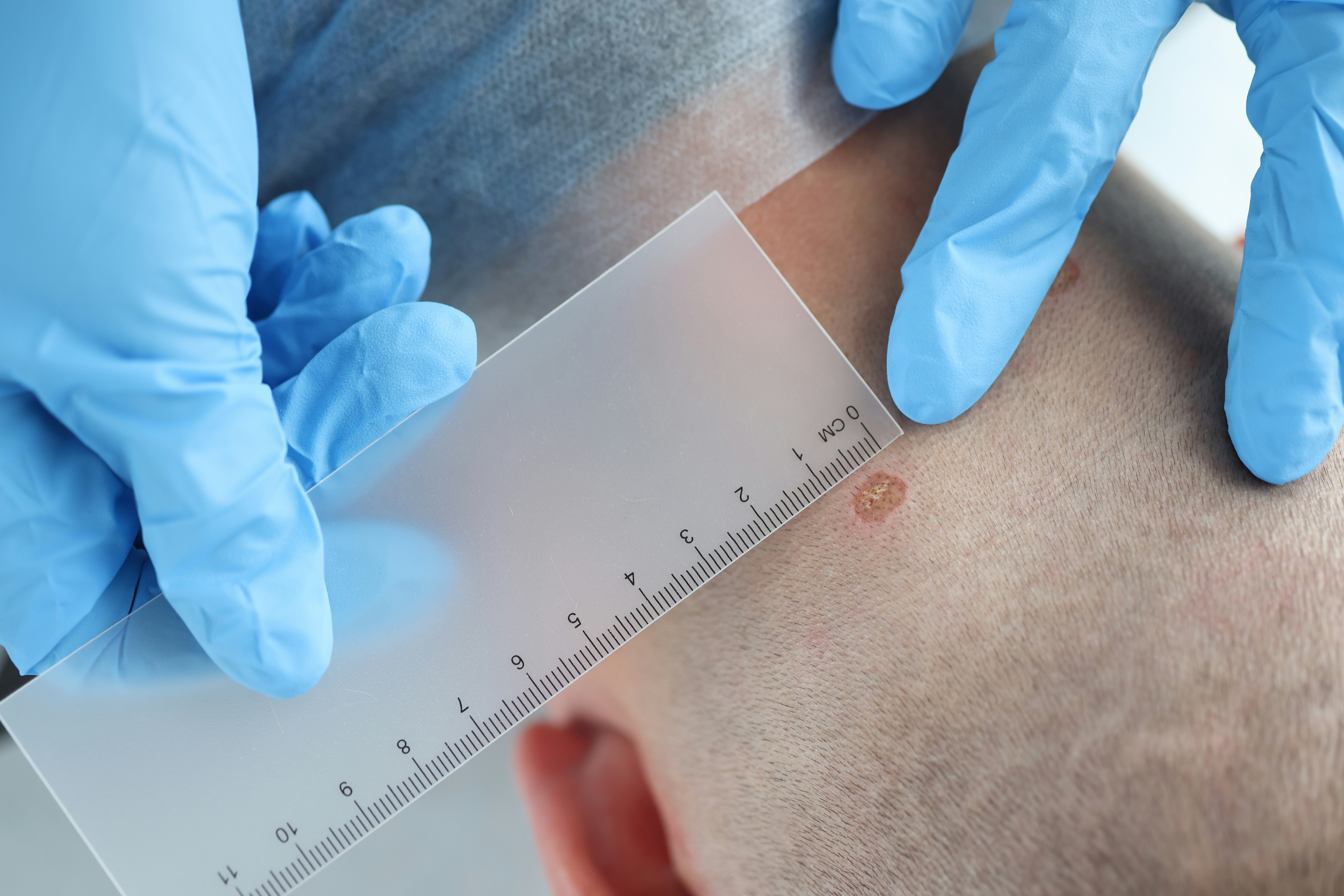
Public awareness is essential in driving early detection. Skin cancer often starts subtly, and many people ignore the early signs until the disease progresses. The ABCDE method is widely used to evaluate suspicious moles and skin changes:
- Asymmetry (irregular shape)
- Border (uneven or blurred edges)
- Color (variation in shades of brown, black, red, or white)
- Diameter (larger than 6mm, about the size of a pencil eraser)
- Evolving (any change in size, color, or shape)
While this method is widely taught, the most important rule is that any new, unusual, or changing skin lesion should be checked by a dermatologist. Early recognition empowers patients to take control of their health before the condition becomes serious.
Risk Factors That Demand Vigilance
Some individuals face higher risks of developing skin cancer. Prolonged sun exposure without protection is the most significant contributor, but other factors include fair skin, light hair, and a family history of skin cancer. Individuals with weakened immune systems, those who frequently use tanning beds, or those with a history of severe sunburns are also more vulnerable. Understanding personal risk is key to taking preventive steps and scheduling regular screenings. For high-risk individuals, annual or biannual dermatology check-ups can make the difference between prevention and late-stage treatment.
Role of Dermatological Screening and Technology
Dermatologists play a central role in identifying skin cancers at their earliest stages. Routine skin examinations, whether conducted by oneself or by a professional, are vital. In recent years, technology has advanced significantly, providing tools like dermoscopy, mole-mapping photography, and artificial intelligence-assisted diagnosis. These methods enable a detailed analysis of skin lesions, facilitating the distinction between benign growths and malignant tumors. Telemedicine has also emerged as a powerful tool, allowing patients to share images with specialists remotely and improving access to early diagnostic care in underserved areas.
Preventive Strategies and Lifestyle Choices
While early detection saves lives, prevention remains the best defense against skin cancer. Practicing sun safety is the foundation of prevention. This includes applying broad-spectrum sunscreen with SPF 30 or higher, wearing protective clothing, and avoiding peak sun hours. Equally important is eliminating artificial tanning, which exposes the skin to concentrated UV radiation. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle that supports immune system strength also contributes to resilience against skin cancer. When prevention and vigilance are combined, individuals can significantly reduce their lifetime risk of developing severe conditions.
Advances in Treatment Linked to Early Detection
When skin cancer is diagnosed early, treatment options are often simpler, less invasive, and highly effective. Surgical removal of the lesion is typically sufficient for early-stage cases, and the procedure can usually be performed in an outpatient setting. Advanced technologies, such as Mohs micrographic surgery, allow for the precise removal of cancerous tissue while preserving healthy skin, thereby improving both cure rates and cosmetic outcomes. In contrast, late-stage cancers may require immunotherapy, radiation, or systemic chemotherapy, all of which can cause side effects and reduce quality of life. Early detection ensures patients have access to the most effective and least disruptive treatments available.
The Global Burden and the Need for Awareness Campaigns
Despite medical progress, skin cancer remains a growing global burden, particularly in regions with high sun exposure. Countries such as Australia and New Zealand report some of the highest incidence rates, but skin cancer is on the rise in Europe, North America, and parts of Asia as well. Public health campaigns that emphasize skin checks, sun safety, and awareness of warning signs have proven effective in reducing mortality. However, more work is needed to reach vulnerable populations and to integrate skin cancer awareness into routine health education. By raising awareness, communities can reduce the stigma associated with seeking help and encourage proactive healthcare behaviors.
Looking Toward the Future: Artificial Intelligence and Genetic Insights
The future of skin cancer management lies in integrating technology with biology. Artificial intelligence is already demonstrating promise in analyzing images of skin lesions with accuracy comparable to that of experienced dermatologists. This could revolutionize screening programs, particularly in remote areas. At the same time, genetic research is uncovering markers that may predict susceptibility to skin cancer, opening the door for personalized prevention strategies. These advances, when combined with traditional awareness campaigns, create a future where skin cancer could be not only treatable but also largely preventable through predictive and precision medicine.
Turning Awareness into Action
Skin cancer may be widespread, but it does not have to be deadly. By recognizing risk factors, practicing prevention, and seeking timely medical advice, individuals can dramatically reduce the dangers associated with this disease. Healthcare providers, policymakers, and communities must continue to emphasize the importance of early detection and promote regular screenings as part of everyday health management. With collective effort, the silent threat of skin cancer can be transformed into a manageable condition where early detection becomes the universal standard of care.